Create Add-In in visual studio
We can extend the existing Visual Studio environment by automation techniques provided by Visual Studio and DotNet framework. We can add our own features to the Visual Studio by creating Add-Ins. Add-In is a complied DLL which run in visual studio IDE.
Here in this blog post we are going to create an Visual Studio Add-In which will;
1. Find and change the name of the Namespace defined in c# source code
2. Find and change the name of the Class defined in c# source code
3. Find and change the name of the Property defined in the c# source code
4. Find and change the name of the function defined in the c# source code
5. Find the attributes defined in a class and if required we can change the values defined inside the attribute
6. Find the attributes of properties defined in a c# source code file.
7. And more over we will be able to iterate through the C# source code and find out the Namespace, Class, Functions, Properties, Delegates, Events and Struct, we can do any kind of manipulation with in the code.
How to create Visual studio Ad-In:
Open VS 2008 got to File Menu -> New -> Project -> Other Project Type -> Extensibility -> Select Visual Studio Add-In
My project name is "VSAddIn". Click on "Ok" you will get the following screen click on next
Select the programming language you use as shown in figure below
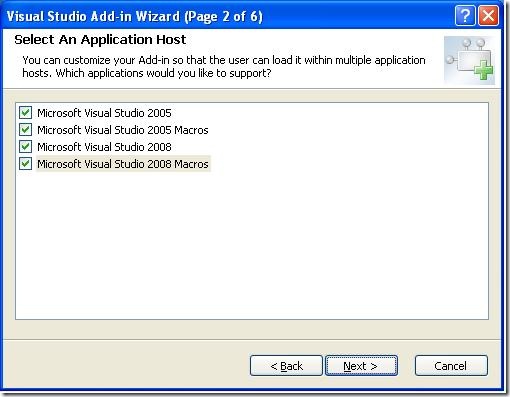
Select the application host as shown in figure below
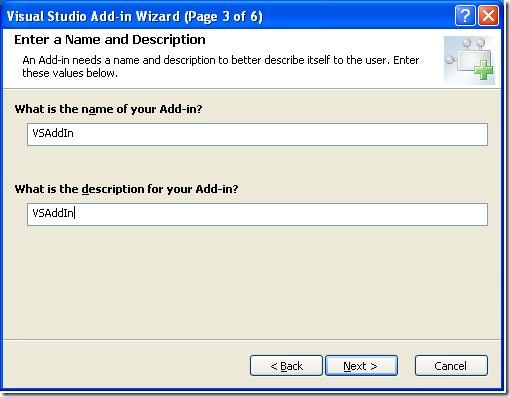
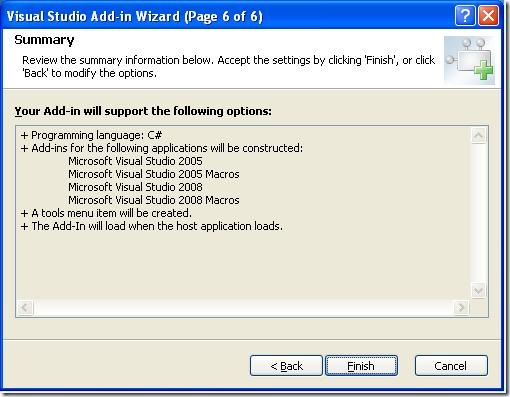
Enter the name and description as shown in below image
You have certain option to configure the way Add-In shows in VS IDE.
Check the first option to show the Add-In in Tools Menu Items
Check the second option to start the Add-In when host application startup
Third one, keep it unchecked
I don't have About information
Finally, Click on finish
Following is my code to implement the above described.
1: public void Exec(string commandName, vsCommandExecOption executeOption, ref object varIn, ref object varOut, ref bool handled)
2: {3: handled = false;
4: if(executeOption == vsCommandExecOption.vsCommandExecOptionDoDefault)
5: {6: if(commandName == "VSAddIn.Connect.VSAddIn")
7: {8: handled = true;
9: // Call the function which will do the code analysis and
10: // modification to your c# code
11: AnalyseAndModifyCode();12: return;
13: } 14: } 15: }
1: private void AnalyseAndModifyCode()
2: {3: foreach (Project project in this._applicationObject.Solution.Projects)
4: {5: foreach (ProjectItem pItem in project.ProjectItems)
6: { 7: AnanlyseAndModifyRecursive(pItem); 8: } 9: } 10: }1: private void AnanlyseAndModifyRecursive(ProjectItem pItem)
2: {3: if (pItem.Name.EndsWith(".cs"))
4: { 5: FileCodeModel2 model = (FileCodeModel2)pItem.FileCodeModel;6: if (model != null)
7: {8: foreach (CodeElement codeElement in model.CodeElements)
9: { 10: ExamineCodeElement(codeElement); 11: } 12: } 13: }14: foreach (ProjectItem pChileItem in pItem.ProjectItems)
15: { 16: AnanlyseAndModifyRecursive(pChileItem); 17: } 18: }1: private void ExamineCodeElement(CodeElement codeElement)
2: {3: try
4: {5: if (codeElement.Kind == vsCMElement.vsCMElementClass)
6: { 7: CodeClass cClass = (CodeClass)codeElement;8: MessageBox.Show("Class name is " + codeElement.Name);
9: 10: foreach (CodeAttribute attr in cClass.Attributes)
11: {12: // Name of the attribute
13: if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(attr.Name))
14: {15: MessageBox.Show("Attributes Defined for class " + codeElement.Name + " is " + attr.Name);
16: }17: // Values Defied in attribute
18: MessageBox.Show("Value of attribute is " + attr.Value);
19: } 20: 21: // To change the name of the class defined in the c# source code file
22: cClass.Name = "NewClassName";
23: }24: if (codeElement.Kind == vsCMElement.vsCMElementProperty)
25: { 26: CodeProperty cProperty = (CodeProperty)codeElement;27: MessageBox.Show("Property name is " + codeElement.Name);
28: foreach (CodeAttribute attr in cProperty.Attributes)
29: {30: if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(attr.Name))
31: {32: MessageBox.Show("Attributes Defined for property " + codeElement.Name + " is " + attr.Name);
33: } 34: } 35: 36: // To change the name of the propert defined in the c# source code file
37: cProperty.Name = "NewClassName";
38: } 39: 40: if (codeElement.Kind == vsCMElement.vsCMElementFunction)
41: { 42: CodeFunction cFucntion = (CodeFunction)codeElement;43: MessageBox.Show("Function name is " + codeElement.Name);
44: 45: foreach (CodeAttribute attr in cFucntion.Attributes)
46: {47: if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(attr.Name))
48: {49: MessageBox.Show("Attributes Defined for function " + codeElement.Name + " is " + attr.Name);
50: } 51: } 52: 53: // To change the name of the property defined in the c# source code file
54: cFucntion.Name = "NewcFucntionName";
55: 56: } 57: 58: if (codeElement.Kind == vsCMElement.vsCMElementNamespace)
59: { 60: CodeNamespace cNamespace = (CodeNamespace)codeElement;61: MessageBox.Show("Namespace name is " + codeElement.Name);
62: 63: // To change the name of the namespace defined in the c# source code file
64: cNamespace.Name = "NewcNameSpaceName";
65: } 66: 67: if (codeElement.Kind == vsCMElement.vsCMElementStruct)
68: { 69: CodeStruct CodeStruct = (CodeStruct)codeElement;70: MessageBox.Show("Struct name is " + codeElement.Name);
71: 72: // To change the name of the Struct defined in the c# source code file
73: CodeStruct.Name = "NewcStructName";
74: } 75: 76: if (codeElement.Kind == vsCMElement.vsCMElementEnum)
77: { 78: CodeEnum CodeEnum = (CodeEnum)codeElement;79: MessageBox.Show("Enum name is " + codeElement.Name);
80: 81: // To change the name of the Enum defined in the c# source code file
82: CodeEnum.Name = "NewcEnumName";
83: } 84: 85: if (codeElement.Kind == vsCMElement.vsCMElementDelegate)
86: { 87: CodeDelegate CodeDelegate = (CodeDelegate)codeElement;88: MessageBox.Show("Delegate name is " + codeElement.Name);
89: 90: // To change the name of the delegate defined in the c# source code file
91: CodeDelegate.Name = "NewcDelegateName";
92: } 93: 94: if (codeElement.Kind == vsCMElement.vsCMElementEvent)
95: { 96: CodeEvent CodeEvent = (CodeEvent)codeElement;97: MessageBox.Show("Event name is " + codeElement.Name);
98: 99: // To change the name of the Event defined in the c# source code file
100: CodeEvent.Name = "NewcEventName";
101: } 102: 103: foreach (CodeElement childElement in codeElement.Children)
104: { 105: ExamineCodeElement(childElement); 106: } 107: }108: catch
109: {110: //
111: } 112: }You can find the complete source code here. The .Zip file contains two projects one is the Add-In application and the other one is a sample project to test the Add-In functionalities.
To test the project first follow the below steps:
1. Build the “VSAddIn” project.
2. Once you build the solution you will get a Add-In File called “VSAddIn.AddIn” in your project folder. Copy the file and got to My Documents –> Visual Studio 2008 –> Add-Ins and paste it there.
3. Edit that Add-In file in notepad. You can find the xml tag <Assembly>Project1.dll</Assembly>. Change the path to the Project1.dll file in you project debug folder. Now open the sample project application go to Tools menu You can find the Add-In “VSAddIn” .
4. Again go back to the Add-In Application project got to Tools Menu Click on Attach process. A number of processes will be listed over there, select the sample project application. Now the Add-In application is ready to debug.
5. Now got to the sample project application and select the “VSAddIn”.
If you need further assistance on how to extend this article according to your need please let me know via comments.
Thanks!!!


2 comments:
Hi there. Do you aware how to get currenly opened file? Or even better get the class where cursor is?
Thanks for the awesome share
Hi we at Colan Infotech Private Limited , a company which is Situated in US and India, will provide you best service and our talented team will assure you best result and we are familiar with international markets, We work with customers in a wide variety of sectors. Our talented team can handle all the aspects of custom application development, we are the best among the dot net development companies in Chennai . asp .net web development company
We have quite an extensive experience working with
asp .net development services. we are the only
asp.net web development company which offer custom services to a wide range of industries by exceeding our client’s expectations. You can even interact directly with the team regarding your project, just as you would with your in-house team. hire asp.net programmers to achieve your dream product.
Custom application development company, asp.net development companies, asp .net web development company,Hire asp .net programmers,asp.net web development services,dot net development companies in chennai
Post a Comment